Introduction
SAP Data Warehouse Cloud is constantly being updated, and even its name has recently changed to SAP Datasphere. With a host of new and modified features, the new version of SAP Datasphere makes it easier for users to manage, model and store data.
Among the recently added features are :
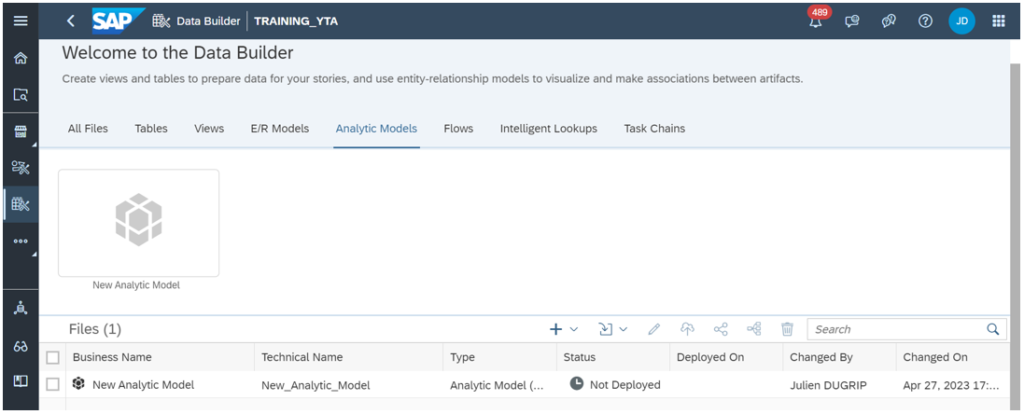
1-ANALYTIC MODELS :
One of SAP Datasphere‘s capabilities is to provide users with exceptional data analysis through interactive dashboards, graphical views and reports using a variety of data sources, including SAP HANA and other third-party data sources.
We typically create Analytical Datasets for this analysis in the Business Builder and then combine the graphical views already created in the Data Builder.
Thanks to Analytic Models, it is now possible to carry out this entire procedure solely in the Data Builder.
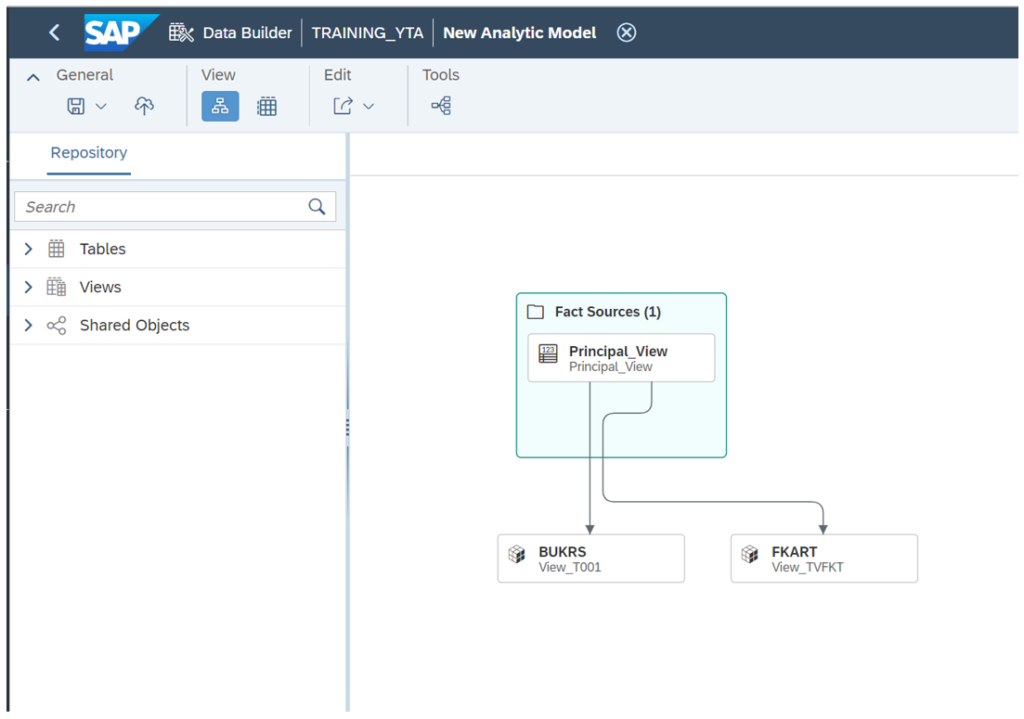
With Analytic Models, users can easily create and manage data flows that automate the process of preparing, transforming and loading data. This facilitates the integration of data from different sources, the cleansing and transformation of data, and finally its loading into Datasets.
The main difference between an Analytic Model and an Analytical Dataset is that the latter is a specific type of dataset optimised for simple analysis. However, the Analytic Model is a broader concept that includes several datasets designed for more complex and advanced analysis tasks.
Subscribe to the Rapid Views Newsletter !
Stay up to date with our latest blog posts, upcoming webinars and news!
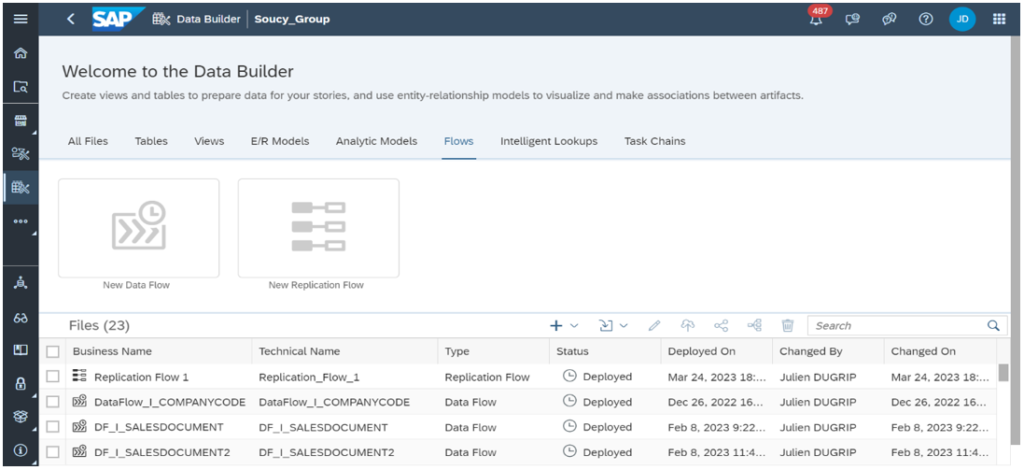
2-REPLICATION FLOW :
The Data Flow functionality we are familiar with is used to copy data from a source system to a target system such as SAP Datasphere. The data can come from different objects in a source system, be it an on-premises system, a cloud-based system, an SAP system, a non-SAP system or different databases. It allows complex data transformations to be applied and integrated into a single output table at a time.
However, Replication Flows offer simple mapping projection options for several objects at once. As a result, we can make one-to-one replications of data from CDS views, tables or ODP providers.
Like Data Flows, Replication Flows are easy to use thanks to a user-friendly interface, as they replicate data without requiring the user to write complex code or scripts. It also enables instant and scheduled data replication, depending on the user’s needs.
To view the Replication Flow functionality in SAP Datasphere, you first need to ensure that your user is assigned the ‘SAP Datasphere Integrator’ role.
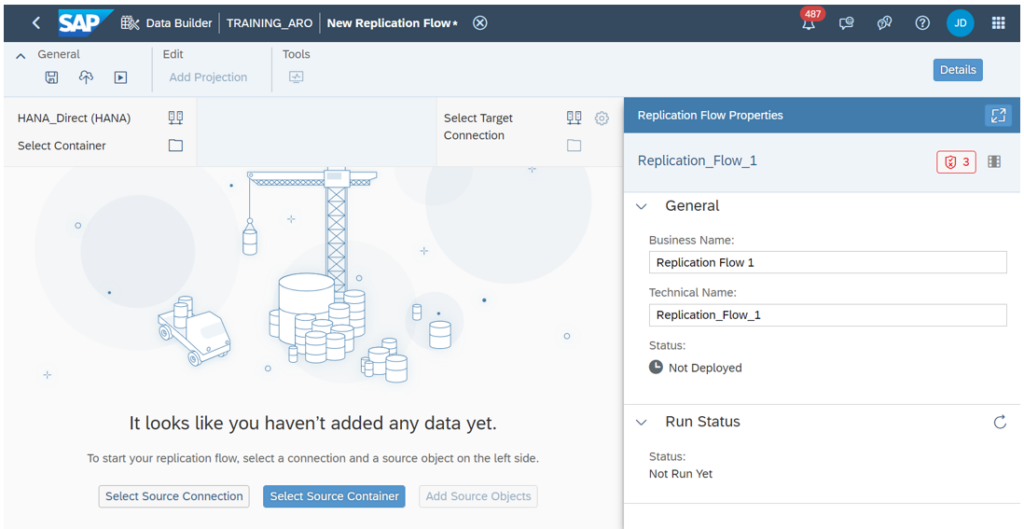
Then create a new Replication Flow. You specify the source system and the target system. The source system can be any system containing data that you want to replicate, whether it’s an on-premises system, a cloud-based system, an SAP system, a non-SAP system or a database. In our case, the target system is SAP Data Warehouse Cloud.

By clicking on “Select Source Connection”, you can choose the source connection from the list of options available in SAP Datasphere.
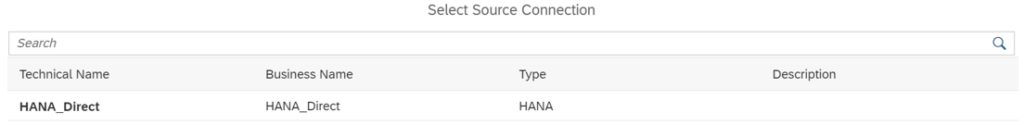
Then you choose an object container:
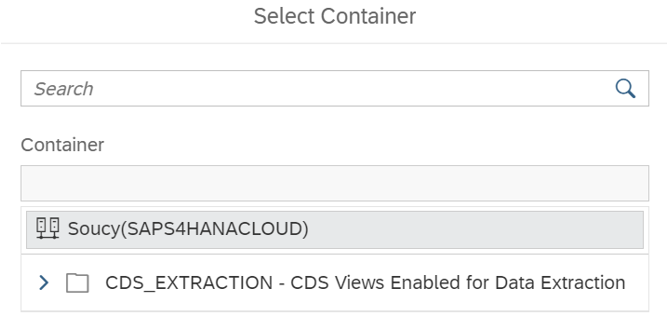
Then select the objects you wish to replicate:
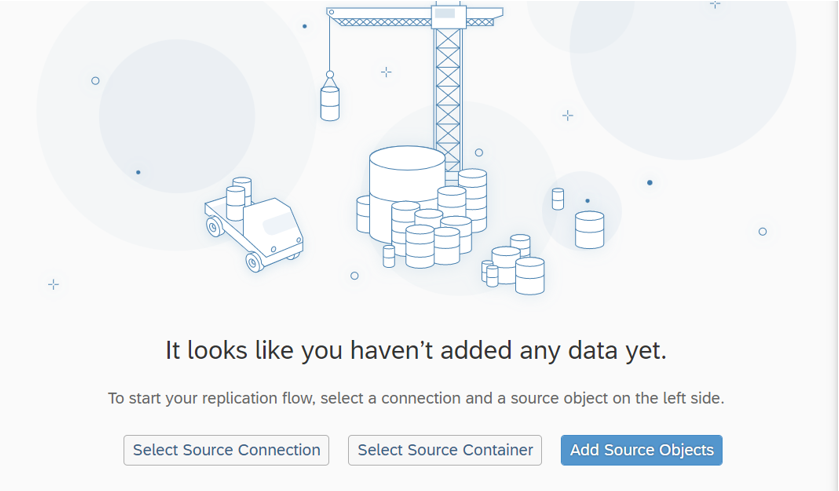
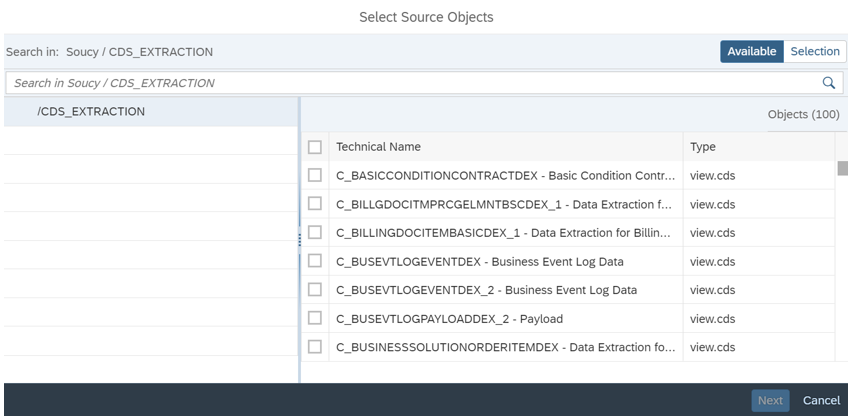
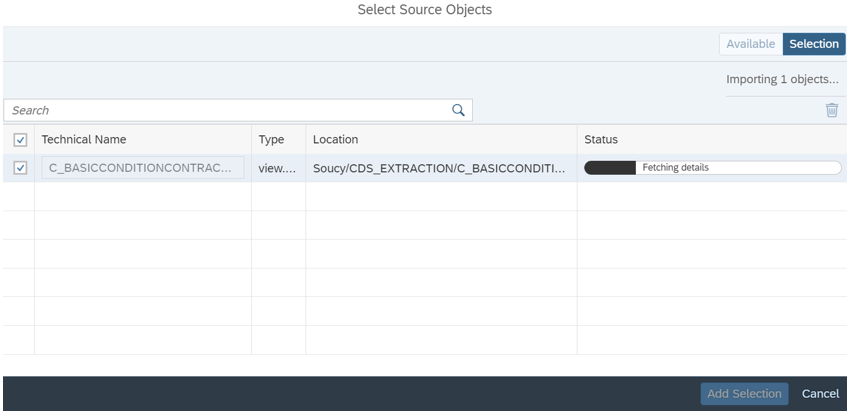
Using the same steps, we select a target connection and map the objects in the source system to the objects previously created in the Data Builder. This mapping will define how the data will be replicated in the target system.
Finally, you can choose the replication mode, either instantaneous or scheduled.
3-CATALOG :
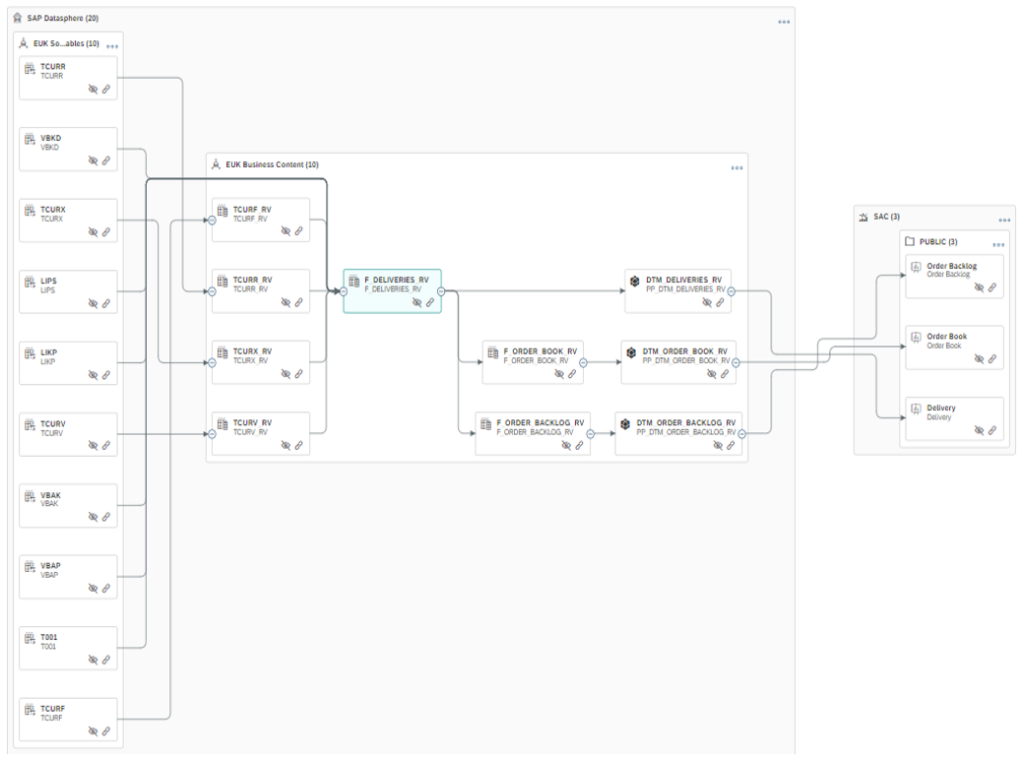
The Catalogue is a centralised repository of all data objects and transformations available in a particular space. It provides a global view of all SAP Dataphere objects. It is the only place where users can discover, understand and manage their objects.
To get this global view, we first create the SAP Datasphere and SAP Analytics Cloud connection on the Monitoring tab.
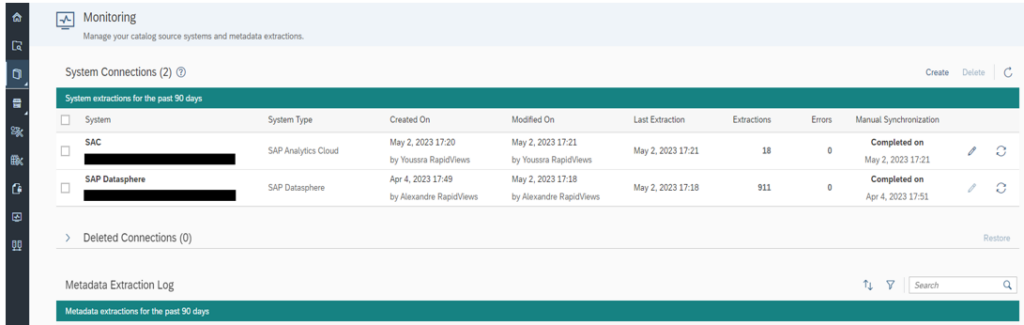
This is where we find the data sources, the connections and the extraction log.
If we synchronise manually, we find the centralised directory as follows:
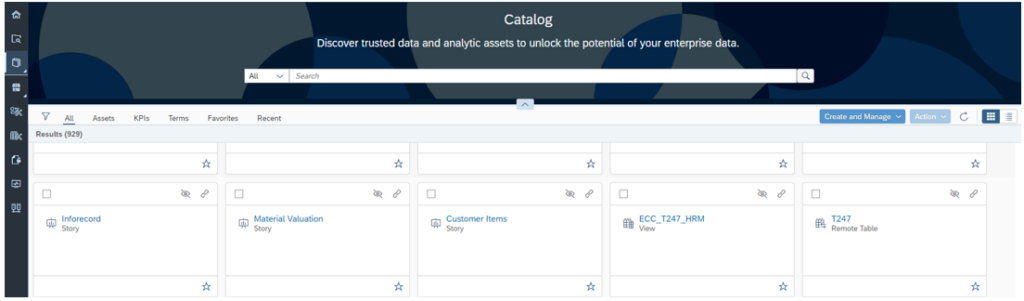
This catalogue features a search bar where users can find what they need, such as views, reports and definitions of either columns, terms or KPIs. In particular, they can search by name, description or tags, and filter results by data type, data source or other attributes.
In this way, the catalogue enables users to find out about the structure and quality of their objects thanks to Data Lineages and dependencies. As a result, users can make reasonable and justified decisions about data consumption.
It also gives the administrator the right to control users and manage their activities. They can limit visibility and change the percentage of access to data.
Conclusion
This article provides an overview of only the newly added features in SAP Datasphere. During each release period, a number of features are modified and enhanced to make the user experience more time and effort efficient.