Introduction
SAP recently unveiled Business Data Cloud, its new unified platform dedicated to data management, processing, and value creation. By bringing together the strengths of SAP Datasphere, SAP HANA Cloud, and Data Fabric capabilities, Business Data Cloud represents a major milestone in the German vendor’s data strategy. This significant evolution aims to reconcile IT, business, and cloud teams around a unified vision of enterprise data.
What is SAP Business Data Cloud?
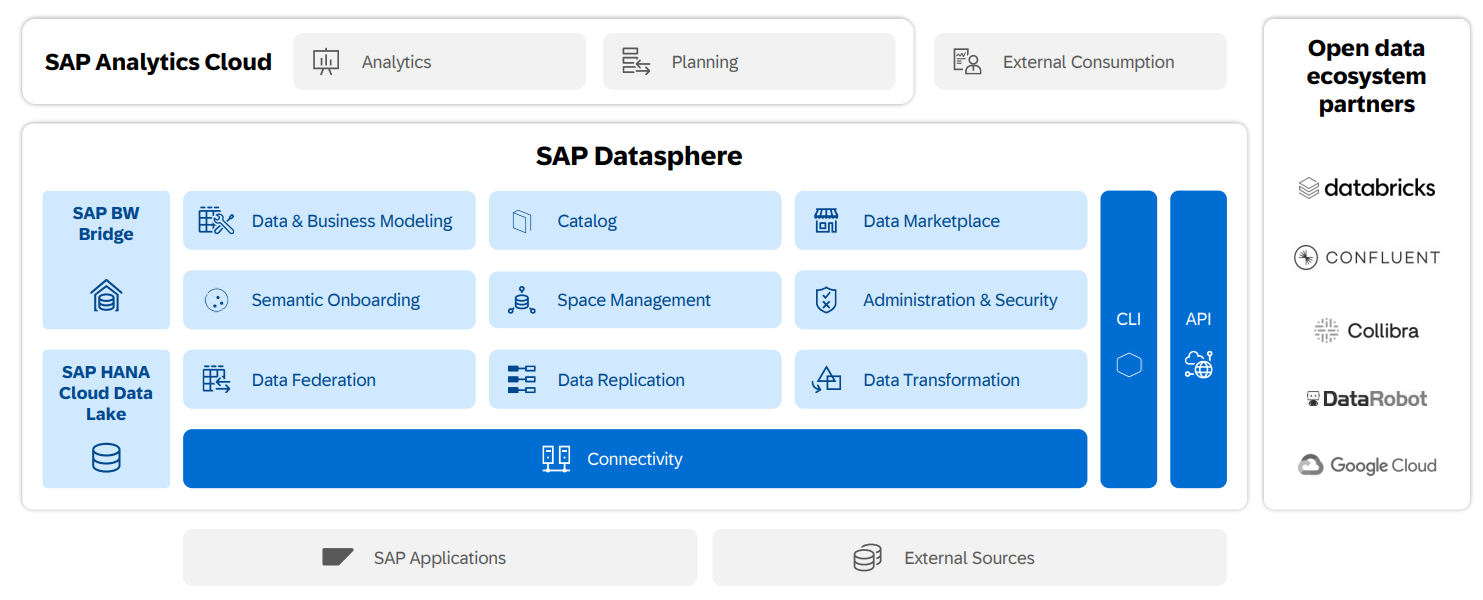
SAP Business Data Cloud is presented as a unified data platform that enables organizations to connect, govern, model, and analyze data across the entire SAP ecosystem—and beyond—within a cloud-first environment.
At its core, it’s an evolution and unification of SAP Datasphere, now enriched with advanced capabilities such as data fabric, data cataloging, business modeling, and data virtualization. It is designed to address the current challenges faced by data and BI leaders:
Real-time access to transactional data without costly replication
Seamless integration with non-SAP data, following a data mesh or data federation approach
Centralized business modeling to ensure KPI consistency
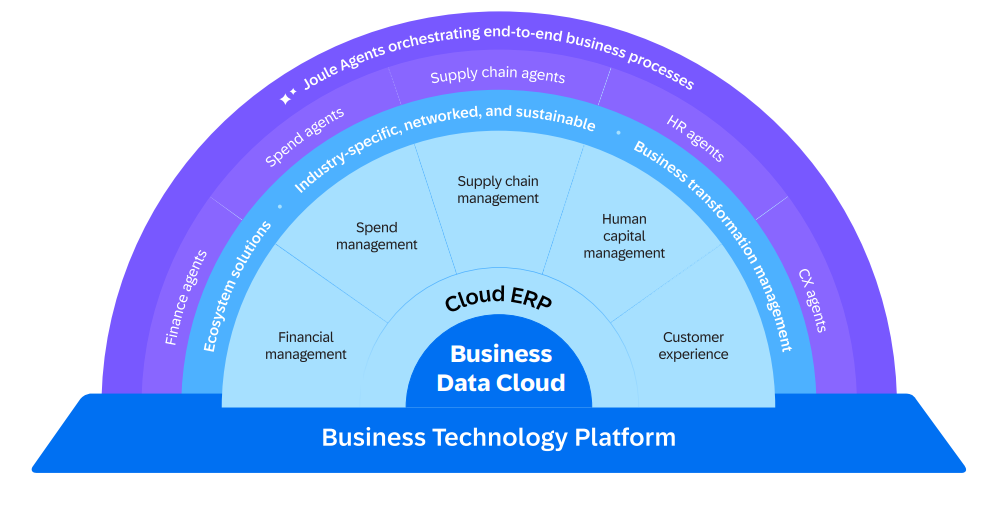
A Strong Promise: Business-Ready Data
SAP’s positioning is clear: it’s not just about storing or aggregating data, but about making it immediately usable by business users—the core idea behind “Business-Ready Data.”
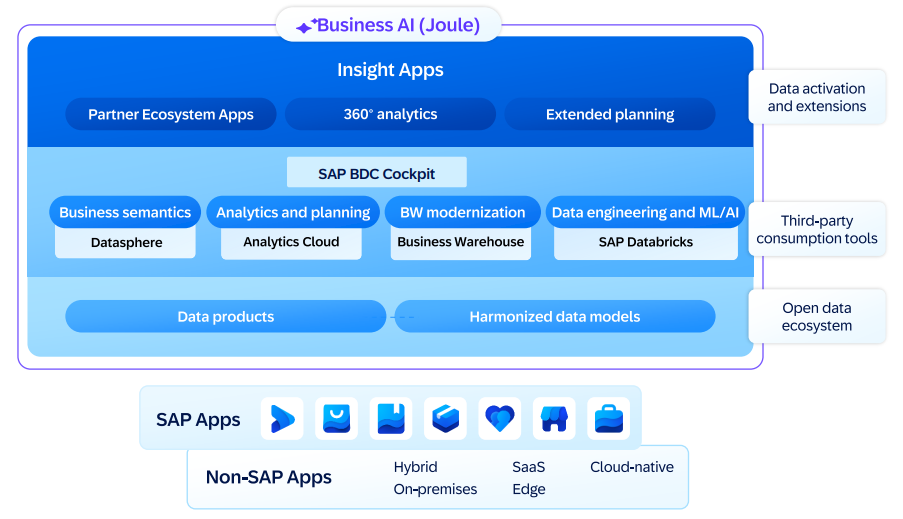
This translates to:
Provision of ready-to-use semantic models, derived from SAP systems (e.g., S/4HANA, Datasphere, SuccessFactors, etc.), as well as from partners like RapidViews through SAP Business Content.
Native connectors that enable seamless access to SAP data while adhering to security and compliance standards.
A redesigned interface allowing business users (controllers, analysts, operational managers) to navigate, understand, and manipulate data independently.
Open and Hybrid Architecture
One of the key strengths of SAP Business Data Cloud is its openness. It’s not limited to the SAP ecosystem—it’s designed to intelligently coexist with hyperscalers (Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, AWS) and analytics tools (like Power BI, Tableau, etc.).
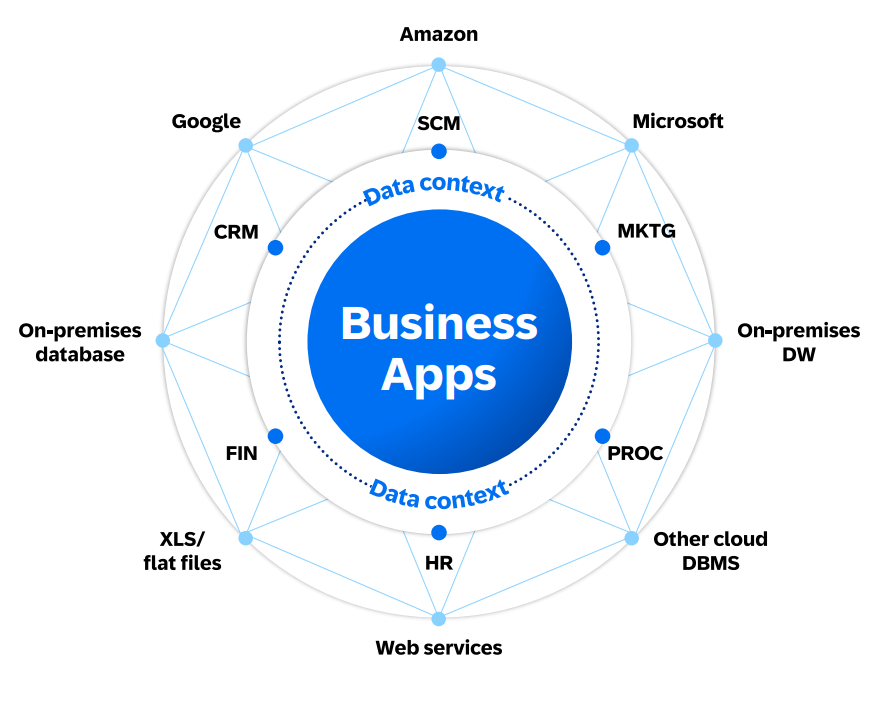
Its data federation capabilities allow companies to combine on-premise, private cloud, and public cloud data sources—without having to move the data. This data fabric approach provides flexibility while maintaining centralized governance.
Key Use Cases
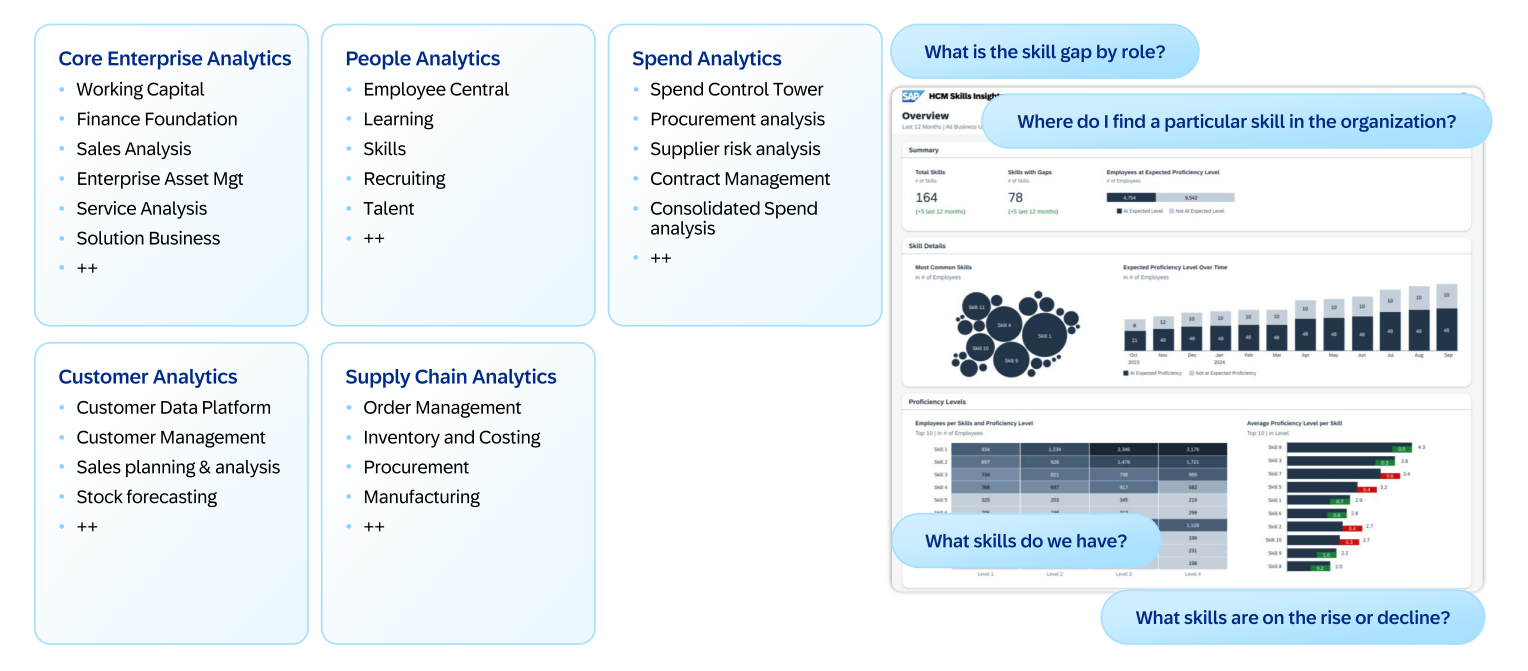
Examples of early use cases targeted by SAP Business Data Cloud include:
Unified financial reporting, combining S/4HANA accounting data with forecasts from other tools
HR performance tracking, aggregating data from SuccessFactors, third-party systems, and internal metrics
Logistics and supply chain monitoring, integrating real-time operational data with cloud-based predictive analytics
Augmented analytics, using SAP Analytics Cloud to create intelligent, dynamic, and collaborative dashboards
Toward a Converged Data & Analytics Strategy at SAP
With Business Data Cloud, SAP aims to both streamline its data offering and deliver a unified experience between operational and analytical systems. This aligns with the broader Data-to-Value vision embraced by next-gen cloud platforms, while leveraging SAP’s strength in business process mastery.
The initiative also supports clean core and modular SAP architectures, empowering enterprises to unlock data value without increasing system complexity.
Cette initiative s’inscrit également dans la dynamique de clean core et de modularisation des SI SAP, en renforçant la capacité des entreprises à valoriser leurs données sans complexifier leur architecture.
Final Thoughts
SAP Business Data Cloud represents a strategic milestone for enterprises seeking to modernize their data landscape while maximizing the value of their SAP investments. By focusing on unification, openness, and business-centric usability, SAP delivers a relevant response to today’s BI challenges. However, the success of this platform will ultimately depend on its ability to quickly deliver tangible value to both IT and business stakeholders.


